Ampholytes 9-11, Servalyt
Carrier ampholytes pH9-11
Applications: Resolve highly basic proteins with isoelectric focusing (IEF) in vertical gels & hoziontal gels, capillary electrophoresis (cIEF) and free-flow electrophoresis
SERVALYT 9-11 carrier ampholytes are useful in identifying acidic and basic isotypes in purified protein samples such as monoclonal antibodies or other biosimilar protein products.
Ampholytes are supplied as 40 % aqueous concentrate and sterile filtered (0.2 μm). If stored at 4 °C and unopened shelf is up to 3 years. The common working concentration is in the range of 3 % to 5 %. Excellent for high resolution of acidic protein in isoelectric focusing (IEF), capillary isoelectric focusing (cIEF) and free flow electrophoresis applications.
Benefits:
-
Available Two Sizes: 10 ml & 25ml
-
High Resolution
-
Fast Staining and Clear Background
-
Ready to Use or Blend
-
3 year shelf life
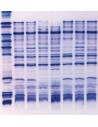
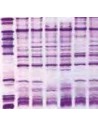
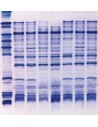
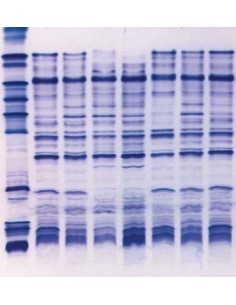
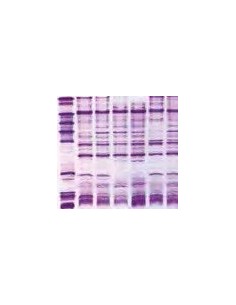
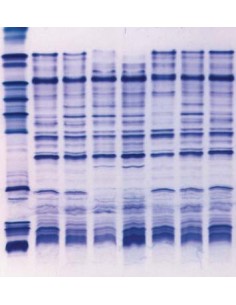
Comparison of different brands of carrier ampholyte
Using an ampholyte pH 9-11 in isoelectric focusing (IEF) offers several applications and benefits, including:
Specific targeting of proteins with pI values in the pH 9-11 range: The pH range of 9-11 allows for the focused separation of proteins with isoelectric points (pI) within this specific range. It is particularly suitable for proteins with moderately basic to highly basic characteristics. By providing a narrow pH gradient, it facilitates the precise migration and focusing of proteins at their respective pI positions, leading to well-resolved bands and improved accuracy in protein analysis.
High-resolution separation: The use of an ampholyte pH 9-11 in IEF enables high-resolution separation of proteins with specific pI values. The narrow pH range enhances the ability to discriminate proteins with similar pI values, resulting in sharper and well-defined protein bands. This enhances the sensitivity and specificity of protein detection, identification, and characterization.
Analysis of specific protein subsets: By focusing on the pH range of 9-11, IEF using an ampholyte pH 9-11 allows for the targeted analysis of specific protein subsets. Certain classes of proteins may have pI values predominantly in this range, such as membrane proteins or histones. This allows researchers to isolate and study these specific proteins within a complex sample mixture.
Protein purification and enrichment: IEF using an ampholyte pH 9-11 can be utilized for protein purification and enrichment. By focusing on the pH range of 9-11, proteins of interest can be separated from other contaminants or unwanted proteins. This facilitates the isolation of specific proteins for downstream applications, such as further analysis or functional studies.
Proteomic profiling: The use of an ampholyte pH 9-11 in IEF is valuable in proteomic profiling studies. By focusing on proteins with pI values in the 9-11 range, researchers can gain insights into specific cellular processes, protein-protein interactions, or disease-related alterations. This targeted profiling allows for a more detailed analysis of proteins within this specific pH range.
Integration with other techniques: IEF using an ampholyte pH 9-11 can be combined with other techniques for comprehensive protein analysis. Following the separation in the first dimension, the resolved proteins can be further analyzed using techniques such as gel electrophoresis, Western blotting, or mass spectrometry, enabling a multi-dimensional approach for protein characterization.
Biomarker discovery and clinical applications: IEF with an ampholyte pH 9-11 can be utilized in biomarker discovery studies. By comparing protein expression profiles between different samples, potential biomarkers associated with specific diseases or conditions can be identified. The focused separation within the pH range of 9-11 allows for the detection of disease-specific protein alterations, aiding in diagnostic and prognostic applications.
In summary, using an ampholyte pH 9-11 in IEF offers targeted separation, high-resolution analysis, specific protein subset analysis, protein purification and enrichment capabilities, proteomic profiling potential, integration with other techniques, and finds application in biomarker discovery and clinical research.
No reviews